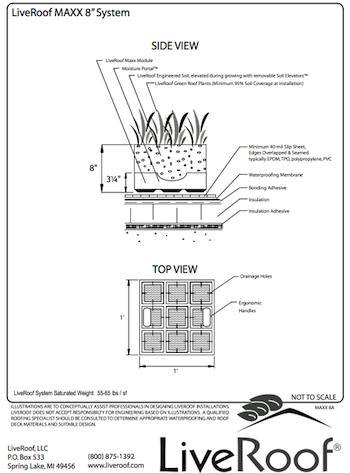
Underfloor Insulation

Underfloor Insulation
While insulating walls, ceilings, and attic spaces seems like a no-brainer to most people, many don't ever stop to think of another area of the home where a great deal of energy loss comes from: the floor.
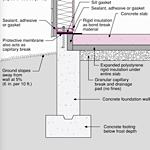
Rigid Underfloor Insulation
A poorly insulated or uninsulated floor can contribute from 15% to 25% of a home's total heat loss, not an insubstantial amount of energy, and money, going right through the floor.
If you're building a home to meet a green certification program such as LEED, underfloor insulation is a must.
If you have a floor that is over a heated space like a finished basement, you don't need to insulate unless you want the soundproofing that insulation provides.
If the floor is over an area that is not heated, such as a crawl space, insulating it can save you a lot in unnecessary energy costs.
What Type of Insulation Can Be Used for Underfloors?
There are several types of insulation available for underflooring; what type you choose depends on how easily accessible the floor joists are, the amount of duct work and wires there are, and the amount of money you want to spend. Like all insulation products, underfloor insulation is most easily installed during a home's construction, but existing homes can also benefit from retrofitting with new insulation.
- Batt Insulation: This is the familiar fiberglass rolled insulation backed with paper. It is one of the most cost effective methods of insulation. Batt insulation may be disadvantageous due to its bulk, making it difficult to install in tight areas or around pipes and wires. Remember, insulation that has to be compressed to fit a space will lose much of its effectiveness.
- Foam Board Insulation: This insulation is a rigid foam board product backed with foil that comes in 4; x 8' sheets. It can be measured and cut outside of the work area to make installation easier. If foam board insulation is used, there will be lots of cracks and seams where the foam board has been cut to fit around obstructions. It will be important to do the extra work to fill and seal all cracks and seams with tape, silicone, or foam spray insulation to ensure maximum performance.
- Blown Insulation: For existing homes, or for areas with lots of hard to reach areas and obstructions, blown insulation is the most effective choice. It will insulate tightly around pipes and wires, and creates a perfect seal. Its' downside is that is is more costly than other options, making its payoff time much longer. Blown insulation is typically installed by a professional due to the equipment needed to blow it in.

Batt Underfloor Insulation

Blown Underfloor Insulation
Underfloor Insulation R-Value
All insulation is rated for its thermal resistance, called the R-Value. The higher the R-Value, the better the insulation with work to improve energy savings. When choosing underfloor insulation, make sure you pay attention to its R-Value, not by its density or if it looks like it would make a good insulation. All of the insulation types above have an R-Value between 3.5 and 4 per inch, and will perform very well if installed properly. The best underfloor insulation choice for your green home is whichever one fits your particular space constraints.Underfloor insulation, working in conjunction with the insulation in the rest of your home, will help keep your indoor spaces comfortable year round, with considerable energy savings that will lighten the load on your wallet.
comments powered by Disqus